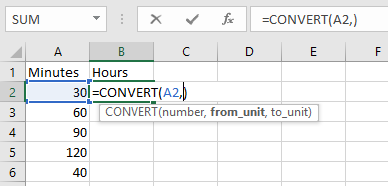
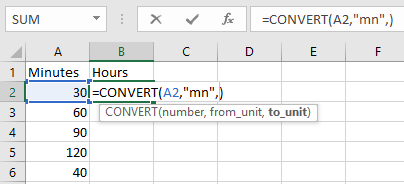
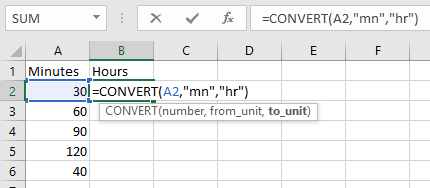
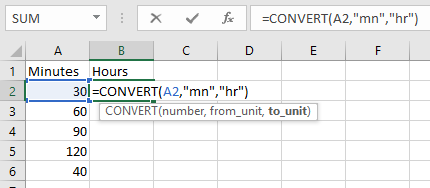
Retrieve Apps password in R12 or Forgot Apps Password in R12
Steps to retrieve forgotten apps password in R12
Step 1 : login to DB-Node
sqlplus / as sysdba
STEP 2 : Create Function for to decrypt the encrypted password
SQL> create FUNCTION apps.decrypt_pin_func(in_chr_key IN VARCHAR2,in_chr_encrypted_pin IN VARCHAR2)
RETURN VARCHAR2
AS
LANGUAGE JAVA NAME 'oracle.apps.fnd.security.WebSessionManagerProc.decrypt(java.lang.String,java.lang.String) return java.lang.String';
/
Function created.
STEP 3 : (Query for password)
SQL> select ENCRYPTED_FOUNDATION_PASSWORD from apps.fnd_user where USER_NAME='GUEST';
Output
ENCRYPTED_FOUNDATION_PASSWORD
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A
STEP 4:
SELECT apps.decrypt_pin_func('GUEST/ORACLE','ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A') from dual;
Output
APPS.DECRYPT_PIN_FUNC('GUEST/ORACLE','ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DEMONSTRATE
STEP 5: (Test apps password)
SQL> conn apps/DEMONSTRATE;
Connected.
CHEERS :)
Steps to retrieve forgotten apps password in R12
Step 1 : login to DB-Node
sqlplus / as sysdba
STEP 2 : Create Function for to decrypt the encrypted password
SQL> create FUNCTION apps.decrypt_pin_func(in_chr_key IN VARCHAR2,in_chr_encrypted_pin IN VARCHAR2)
RETURN VARCHAR2
AS
LANGUAGE JAVA NAME 'oracle.apps.fnd.security.WebSessionManagerProc.decrypt(java.lang.String,java.lang.String) return java.lang.String';
/
Function created.
STEP 3 : (Query for password)
SQL> select ENCRYPTED_FOUNDATION_PASSWORD from apps.fnd_user where USER_NAME='GUEST';
Output
ENCRYPTED_FOUNDATION_PASSWORD
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A
STEP 4:
SELECT apps.decrypt_pin_func('GUEST/ORACLE','ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A') from dual;
Output
APPS.DECRYPT_PIN_FUNC('GUEST/ORACLE','ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DEMONSTRATE
STEP 5: (Test apps password)
SQL> conn apps/DEMONSTRATE;
Connected.
CHEERS :)
Step 1 : login to DB-Node
sqlplus / as sysdba
STEP 2 : Create Function for to decrypt the encrypted password
SQL> create FUNCTION apps.decrypt_pin_func(in_chr_key IN VARCHAR2,in_chr_encrypted_pin IN VARCHAR2)
RETURN VARCHAR2
AS
LANGUAGE JAVA NAME 'oracle.apps.fnd.security.WebSessionManagerProc.decrypt(java.lang.String,java.lang.String) return java.lang.String';
/
Function created.
STEP 3 : (Query for password)
SQL> select ENCRYPTED_FOUNDATION_PASSWORD from apps.fnd_user where USER_NAME='GUEST';
Output
ENCRYPTED_FOUNDATION_PASSWORD
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A
STEP 4:
SELECT apps.decrypt_pin_func('GUEST/ORACLE','ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A') from dual;
Output
APPS.DECRYPT_PIN_FUNC('GUEST/ORACLE','ZG37E123746712BDB2D99E048FE44AE662F2713E2EDB443391BABA0414CADDB7A2E6DD45BBAFA7270A663E5EEBA837F5548A')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DEMONSTRATE
STEP 5: (Test apps password)
SQL> conn apps/DEMONSTRATE;
Connected.
CHEERS :)